Botanicum: Welcome to the Museum

Plants and botany hold a vital place in our world. Understanding plant life enriches knowledge and fosters appreciation for nature. Botanicum, a remarkable edition by Katie Scott and Kathy, offers a vivid exploration of this field. The Academy of Botany reveals that almost 40% of global land plant species face extinction risks. Botanicum by Katie Scott, part of the Big Picture Press series, serves as a gateway to this fascinating realm. The connection between plants and human life is profound, with Botanicum illustrating this beautifully.
The Basics of Botany
Definition and Scope

What is Botany?
Botany explores plant life. This field examines the structure, growth, reproduction, metabolism, development, diseases, and chemical properties of plants. Scientists study how plants interact with their environment. Botany plays a crucial role in understanding ecosystems and biodiversity.
Branches of Botany
Botany includes various branches. Plant physiology focuses on plant functions. Plant ecology examines interactions within ecosystems. Plant taxonomy classifies plants. Each branch contributes to a comprehensive understanding of plant life.
Historical Background
Early Studies
Early studies of plants date back to ancient civilizations. Scholars documented plant uses for medicine and agriculture. Theophrastus, an ancient Greek philosopher, made significant contributions. His work laid the foundation for modern botany.
Key Figures in Botany
Theophrastus earned the title "Father of Botany." His extensive studies provided insights into plant classification and function. Many botanists followed his path. These pioneers expanded knowledge and inspired future generations.
Plant Anatomy and Physiology
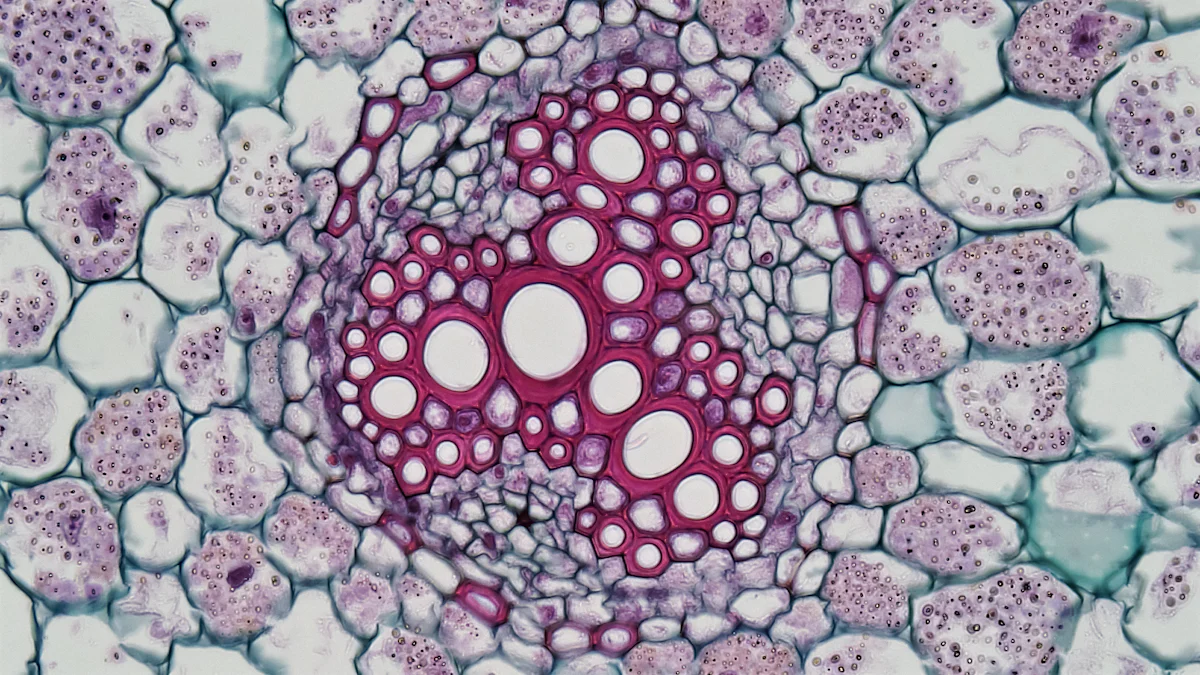
Structure of Plants
Roots and Their Functions
Roots anchor plants in the soil. Roots absorb water and nutrients. Roots store food for future use. Different root types serve specific purposes. Taproots grow deep to access water. Fibrous roots spread out for stability.
Stems and Leaves
Stems support plants. Stems transport water and nutrients. Stems contain xylem and phloem tissues. Leaves capture sunlight. Leaves perform photosynthesis. Leaves have stomata for gas exchange.
Photosynthesis and Growth
The Process of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis converts sunlight into energy. Chlorophyll in leaves absorbs light. Plants use carbon dioxide and water. Plants produce glucose and oxygen. This process sustains plant life.
Factors Affecting Growth
Several factors influence plant growth. Light intensity affects photosynthesis. Water availability impacts nutrient uptake. Soil quality determines root health. Temperature regulates metabolic rates. Understanding these factors aids cultivation.
Plant Diversity and Classification
Types of Plants
Flowering vs. Non-Flowering Plants
Flowering plants, known as angiosperms, produce flowers and seeds enclosed within fruits. These plants dominate most ecosystems. Non-flowering plants, such as ferns and mosses, reproduce through spores. These plants do not produce flowers or seeds. Understanding these differences helps identify plant species.
Trees, Shrubs, and Herbs
Trees have a single woody stem and grow tall. Shrubs have multiple stems and remain shorter than trees. Herbs possess soft stems and complete their life cycle quickly. Each type plays a unique role in ecosystems. Recognizing these categories aids in plant identification.
Classification Systems
Linnaean System
The Linnaean System classifies plants into hierarchical categories. This system starts with the Kingdom and narrows down to Variety. Carl Linnaeus developed this method in the 18th century. The system provides a structured way to name and organize plants.
Modern Taxonomy
Modern taxonomy incorporates genetic information. Scientists use DNA analysis to classify plants more accurately. This approach updates traditional methods. Modern taxonomy reflects evolutionary relationships among plants. Understanding these systems enhances knowledge of plant diversity.
The Role of Plants in the Ecosystem
Ecological Importance
Oxygen Production
Plants play a crucial role in producing oxygen. Photosynthesis allows plants to convert carbon dioxide into oxygen. This process sustains life on Earth. Every breath you take depends on this vital function. Forests and oceans contribute significantly to global oxygen levels. Protecting these areas ensures a healthy atmosphere.
Habitat and Food Source
Plants provide essential habitats for countless species. Forests, grasslands, and wetlands offer shelter and food. Animals rely on plants for survival. Birds nest in trees. Insects feed on leaves. Mammals find refuge in dense vegetation. Preserving plant diversity supports entire ecosystems. Conservation efforts must prioritize plant-rich areas.
Human Benefits
Medicinal Uses
Plants have been used in medicine for centuries. Many modern drugs originate from plant compounds. Aspirin comes from willow bark. Quinine, used to treat malaria, derives from cinchona trees. Herbal remedies offer natural healing options. Research continues to discover new medicinal properties. Protecting plant diversity ensures future medical breakthroughs.
Agricultural Importance
Agriculture relies heavily on plants. Crops provide food for billions. Wheat, rice, and corn are staple foods worldwide. Farmers cultivate plants for fiber, oil, and biofuels. Sustainable farming practices enhance soil health. Crop rotation and organic methods reduce environmental impact. Supporting agriculture ensures food security for future generations.
Scientific Research Findings:
Conservation of Plant Diversity and Human Benefits: Plants are essential for human survival and well-being.
Importance of Plant Conservation for Human Survival: Plants synthesize oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Vital Importance of Plant Conservation and Bio Plant Cellicitation Technology: New technologies reduce environmental impact.
Contemporary Relevance of Botany
Botany continues to evolve, playing a critical role in addressing global challenges. The field's contemporary relevance lies in its efforts to conserve plant diversity and harness technological advances.
Conservation Efforts
Protecting Endangered Species
Efforts to protect endangered species have become more urgent. Many plant diversity hotspots exist outside protected areas. This situation demands immediate action. Conservationists prioritize these regions to safeguard biodiversity. Public gardens contribute significantly by maintaining conservation collections. These collections help preserve threatened species. The Global Assessment of Plant Conservation Status highlights the need for targeted conservation. Plants face threats from global warming and habitat destruction. Cataloging the world's flora becomes essential. Protecting plants from overcollecting ensures their survival.
Sustainable Practices
Sustainable practices in botany promote environmental health. Researchers develop strategies to minimize human impact on ecosystems. Conservationists advocate for sustainable agriculture. Crop rotation and organic farming reduce soil degradation. These methods enhance soil fertility. Sustainable practices extend to forestry and urban planning. Green spaces in cities improve air quality. Urban forests provide habitats for wildlife. Communities benefit from these green initiatives. Sustainable practices ensure a balanced relationship between humans and nature.
Technological Advances
Genetic Engineering
Genetic engineering revolutionizes plant science. Scientists manipulate plant genes to enhance traits. Crops become more resistant to pests and diseases. Genetic modifications improve nutritional content. Farmers achieve higher yields with fewer resources. Genetic engineering supports food security. This technology addresses the challenges of a growing population. Innovations in genetic engineering continue to emerge. Researchers explore new possibilities for plant improvement.
Innovative Research
Innovative research transforms botany. Technologies like DNA sequencing and artificial intelligence drive progress. Scientists use robotics and 3D printing in plant studies. These tools expand the understanding of plant life. The University of Kansas focuses on phylogenetics and environmental change. Interdisciplinary approaches enrich research outcomes. Standardized data collection enhances collaboration. The Denver Botanic Gardens leads efforts in this area. Data sharing benefits the scientific community. Innovative research paves the way for a sustainable future.
American Industrial Art influences botany through design and technology. The American Industrial Art Series showcases the intersection of art and science. Contemporary American Industrial Art inspires new approaches in plant conservation. Artists like Anselm Kiefer explore themes of nature and industry. Kiefer's work reflects the complex relationship between humans and the environment. These artistic expressions enrich the understanding of botany.
Botanical Art and Herbaria
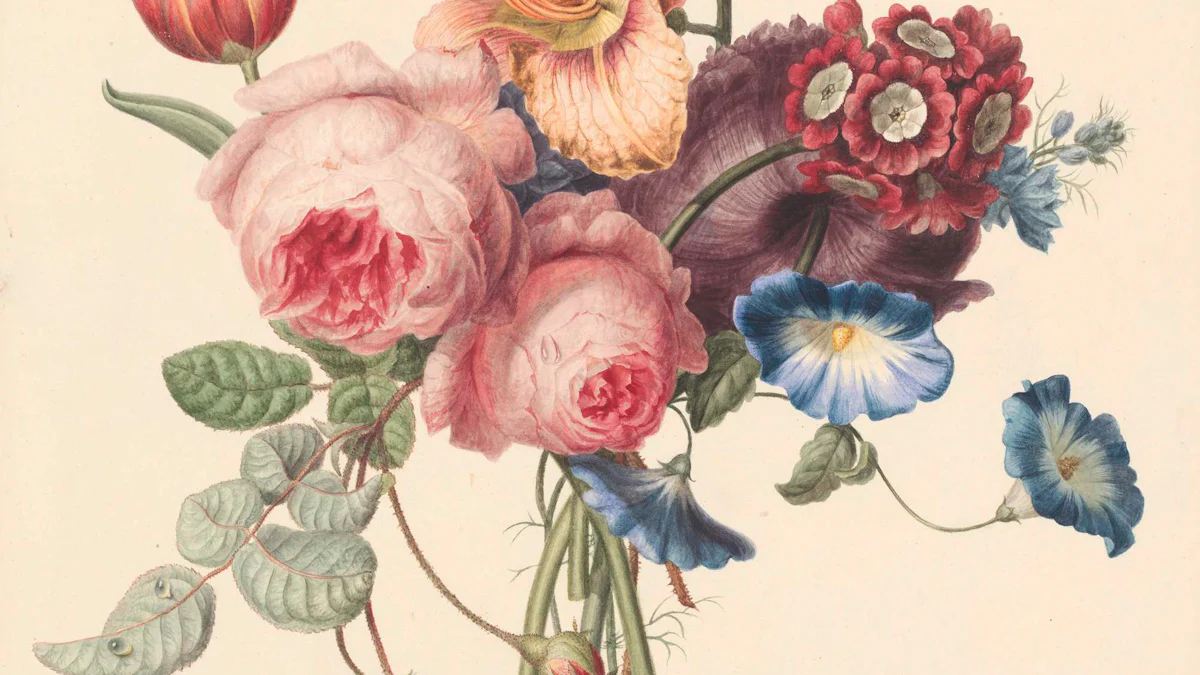

The Role of Art in Botany
Botanical Illustrations
Botanical illustrations capture the beauty and complexity of plant life. Artists use these illustrations to convey detailed information about plants. The Metropolitan Museum showcases many botanical artworks. These illustrations often rely on Herbarium specimens for accuracy. The Chicago Academy emphasizes the importance of such illustrations. Botanical art serves as a bridge between science and creativity. Gardenista highlights how artists depict plants with precision. Illustrations provide valuable insights into plant anatomy. Many artists draw inspiration from Herbaria collections.
Art as a Tool for Education
Art plays a crucial role in educating the public about botany. Museums like the Manchester Museum use art to engage visitors. Educational programs often incorporate botanical art. The National Gallery of Victoria features exhibits that teach about plant diversity. Remodelista explores how art enhances understanding of plant ecosystems. Art helps simplify complex scientific concepts. Herbarium World uses art to inspire curiosity about plants. Botanical art encourages appreciation for nature's diversity. The Metropolitan Museum of Art offers workshops on botanical illustration. Art fosters a deeper connection with the natural world.
Understanding Herbaria
Definition and Purpose
Herbaria serve as vital repositories for plant specimens. Scientists use Herbaria to study plant diversity and distribution. The Academy of Sciences’ collections include thousands of specimens. Herbarium specimens provide historical records of plant life. Researchers rely on these collections for taxonomic studies. Herbaria document changes in plant populations over time. The Museum of Natural History houses extensive Herbarium archives. Herbaria play a key role in conservation efforts. The Green Plant Herbarium focuses on preserving endangered species.
Importance in Research and Conservation
Herbaria contribute significantly to research and conservation. Scientists analyze Herbarium specimens to understand environmental changes. Herbaria support efforts to protect threatened plant species. The Chicago Academy collaborates with other institutions for conservation. Herbarium World highlights the role of herbaria in biodiversity studies. Academy of Sciences’ effort ensures the preservation of plant data. Herbaria aid in identifying new plant species. Gardenista discusses the impact of herbaria on ecological research. Herbaria serve as educational resources for students and researchers. Remodelista family of websites explores the intersection of art and science in herbaria.
Plants and botany hold immense importance for human survival. Plants provide food, medicine, and oxygen. The role of plants in maintaining ecosystem balance is undeniable. You must explore and appreciate plant life. Understanding plants enriches knowledge and fosters a connection with nature. Conservation efforts are crucial to protect plant species from threats like habitat destruction. Sustainable practices ensure the survival of plants for future generations. You can contribute by supporting conservation initiatives. Embrace the beauty of plants and their vital role in our world.
See Also
Plant and Fungi Knowledge Encyclopedia

